In the ever-changing management theories, contingency theory becomes one of the most prominent ideas about flexibility and adaptability. It proposes that there cannot be a one-size-fits-all approach to managing an organization. In its place, it suggests that effective management has to rely on a couple of situational factors that impact organizational behavior. This article tries to discuss the contingency theory, its application in management, and real-life examples explaining its importance.
What is Contingency Theory?
Developed in the 1960s, contingency theory challenges the concept that management strategies can be one-size-fits-all. According to this theory, what will be best for a business or an organization is contingent upon the internal and external factors it has to meet. The first theorists to pioneer this theory were Fred Fiedler, Paul Lawrence, Jay Lorsch, and Joan Woodward, who developed it from their respective viewpoints.
Key Components of Contingency Theory
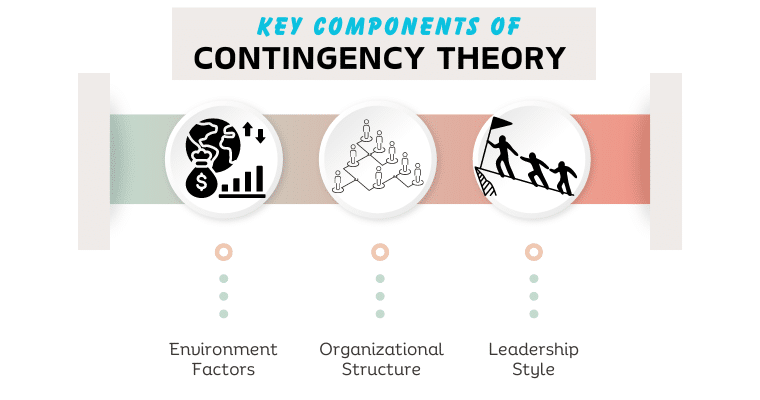
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors are the external elements that appear to have an impact on organizational performance. They will include such factors as market dynamics, economic conditions, technological changes or advancements, and regulatory changes. It holds that managers must consider these factors when strategizing or making decisions.
Organizational Structure
The type of organizational structure should be consistent with the organization’s goals, size, and environment. According to Joan Woodward, technological complexity determines the optimum organizational structure. For instance, the bureaucratic structure benefits in the case of mass production firms, while innovative companies like to work in less formal environments.
Leadership Style
According to Fred Fiedler’s contingency model, leadership styles should be matched with situational demands. He distinguished two major styles of leadership: task-oriented and relationship-oriented. Each style is in turn contingent upon leader-member relationships, task structure, and positional power.
Some Important Theories
Fiedler’s Contingency Theory
Probably the most famous application of CT is Fred Fiedler’s contingency theory of leadership. He suggested that effectiveness is contingent upon the interaction between their leadership style and the favorableness of the situation. He came up with the Least-Preferred Coworker scale to estimate a leader’s orientation toward tasks or relations. For Fiedler, neither style is inherently better; rather, the key is to match the leader’s style with the right situational context.
Contingency Theory of Leadership
The contingency theory of leadership is far broader than Fiedler’s model encompassing a range of approaches that stress context as the determinant factor of effective leadership. Contingency leadership requires style flexibility and adaptability according to the needs presented by the followers and the demands of the situation. Other notable models include Hersey and Blanchard’s Situational Leadership Theory and Vroom and Yetton’s Normative Decision Model.
Contingency Theory of Management
The contingency theory of management broadens the principles of contingency thinking into general organizational practice. This approach suggests that management practices, together with organizational structures, need to be attuned to the situation of each particular entity. In choosing management practices, consideration, therefore, has to be given to such factors as organizational size, technology, and environmental uncertainty.
Contingency Theory in Psychology
Contingency theory in psychology refers to changes in human behavior respecting situational factors. This framework has been applied to a myriad of psychological phenomena, from motivation to learning to decision-making. Based on the current contingencies at play, psychologists could use such a framework to better predict and therefore influence behavior.
You may also Read: Concept of Servant Leadership
Application of Contingency Theory
Strategic Planning
It is important in strategic planning because it forces one, as a manager, to consider the external and internal factors before strategy formulation. This adaptiveness will ensure a quick response by the organization whenever there is a change in the business environment.
Crisis Management
It provides the framework for flexible decision-making during a crisis. The managers could modify their strategy concerning the nature of the crisis and the availability of resources at their command. This adaptability will become very important in reducing damage and restoration of normalcy.
Human Resource Management
It contributes to human resource management in the sense that HR practices must be flexible. This concerns the application of recruitment, training, and performance evaluation strategies in a manner relevant to a given organizational setup and environment.
Real-World Examples
Apple Inc.
Apple has been able to adapt its managing practices concerning changing market conditions. It has been able to sustain quite an innovative culture with a non-bureaucratic organizational structure that has enabled it to respond rather quickly to the changes in technology and consumer tastes. The contingency approach in Apple is quite apparent in the product development strategies and global supply chain management process adopted by the organization.
Toyota
The case of the production system, as typified by Toyota, represents an efficient and flexible way of production—otherwise, contingency theory in practice. The company changes the structure of its production, as required by the market demand and economic situation, and thereby manages to remain the top one in the field of automobile manufacturing.
How to Implement Contingency Theory
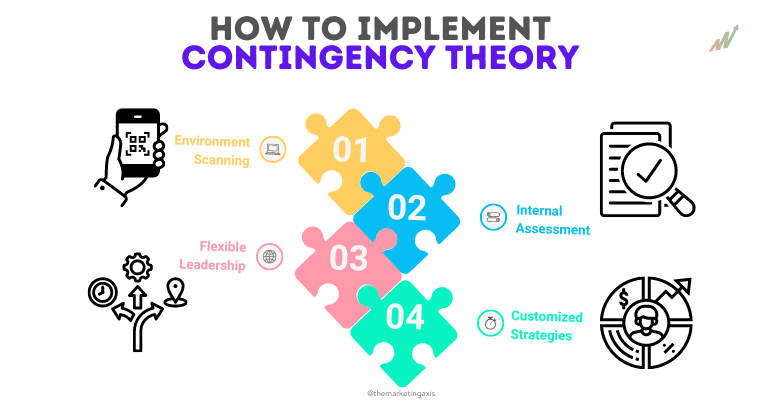
Environmental Scanning
Organizations should monitor their external environment at every point in time to identify opportunities and threats entailed. Similarly, It is a proper assessment of market trends, the activities of competition, changes in rules and regulations, and technological growth.
Internal Assessment
An internal evaluation enables an organization to perceive its strengths and weaknesses. This means looking at the company in terms of its resources, capabilities, and other aspects of performance. The insights drawn from this evaluation form the basis for strategic decisions.
Flexible Leadership
The leader has to be versatile and thus in a position to change his management style with time. This could be a change from task-oriented to relationship-oriented, depending on the needs of the team and the problems encountered.
Customized Strategies
Organizations at each particular level have to develop strategies that best fit their context. This means it: marketing, production, and HR practices have to be tailored to the organization’s environment and goals.
Conclusion
Contingency theory offers a valuable viewpoint on management, putting forward adaptability and situation awareness. Using this knowledge and recognizing the principles underpinning CT, strategies can be made within an organization to fit the particular context and develop sustained success in that specific environment. Likewise, from strategic planning and crisis management to human resource practice, the application of contingency theory aids in guiding organizations through the modern business world.
FAQs about Contingency Theory
1. What is the primary focus of contingency theory?
The contingency theory is thus based on the principle that there is no ideal way of managing an organization. Instead, situational factors drive the best course of action.
2. How does contingency theory differ from traditional management theories?
Traditional management theories often support the view that certain principles can be universally applied. According to the CT, principles are supposed to be flexible and adapted to circumstances.
3. Can contingency theory be applied to all types of organizations?
Yes, contingency theory is versatile and applicable to all kinds of organizations: businesses, non-profit making organizations, and governmental entities.
4. What are some challenges in implementing contingency theory?
The challenge in implementing contingency theory is, that the application of CT is tricky, for it requires constant environmental scanning. Likewise, flexible leadership, and the development of strategies that are issues-specific. Thus, it requires deep knowledge about internal and external factors influencing the organization.
5. Why is contingency theory important in today’s business environment?
The contemporary business environment is very dynamic, and an organization has to adapt itself continuously to the changing situation. It offers a framework for flexibility in decision-making that allows a proper response to new challenges and opportunities.
References
- Fiedler, F. E. (1967). A Theory of Leadership Effectiveness. McGraw-Hill.
- Lawrence, P. R., & Lorsch, J. W. (1967). Organization and Environment: Managing Differentiation and Integration. Harvard Business School Press.
- Woodward, J. (1965). Industrial Organization: Theory and Practice. Oxford University Press.
- Robbins, S. P., & Coulter, M. (2018). Management (13th ed.). Pearson Education.
- Apple Inc. (2023). Annual Report. Retrieved from Apple’s official website.
- Toyota Motor Corporation. (2023). Production System Overview. Retrieved from Toyota’s official website.