Almost every business wants to move beyond its national contour with the power of globalization at work in today’s business. Approaching international business has its share of problems. Some influential factors such as culture, administration, geography, and economics create massive challenges for companies entering a new market. International business strategists overcome all these complexities with frameworks like the CAGE distance framework.
What is the CAGE Distance Framework?
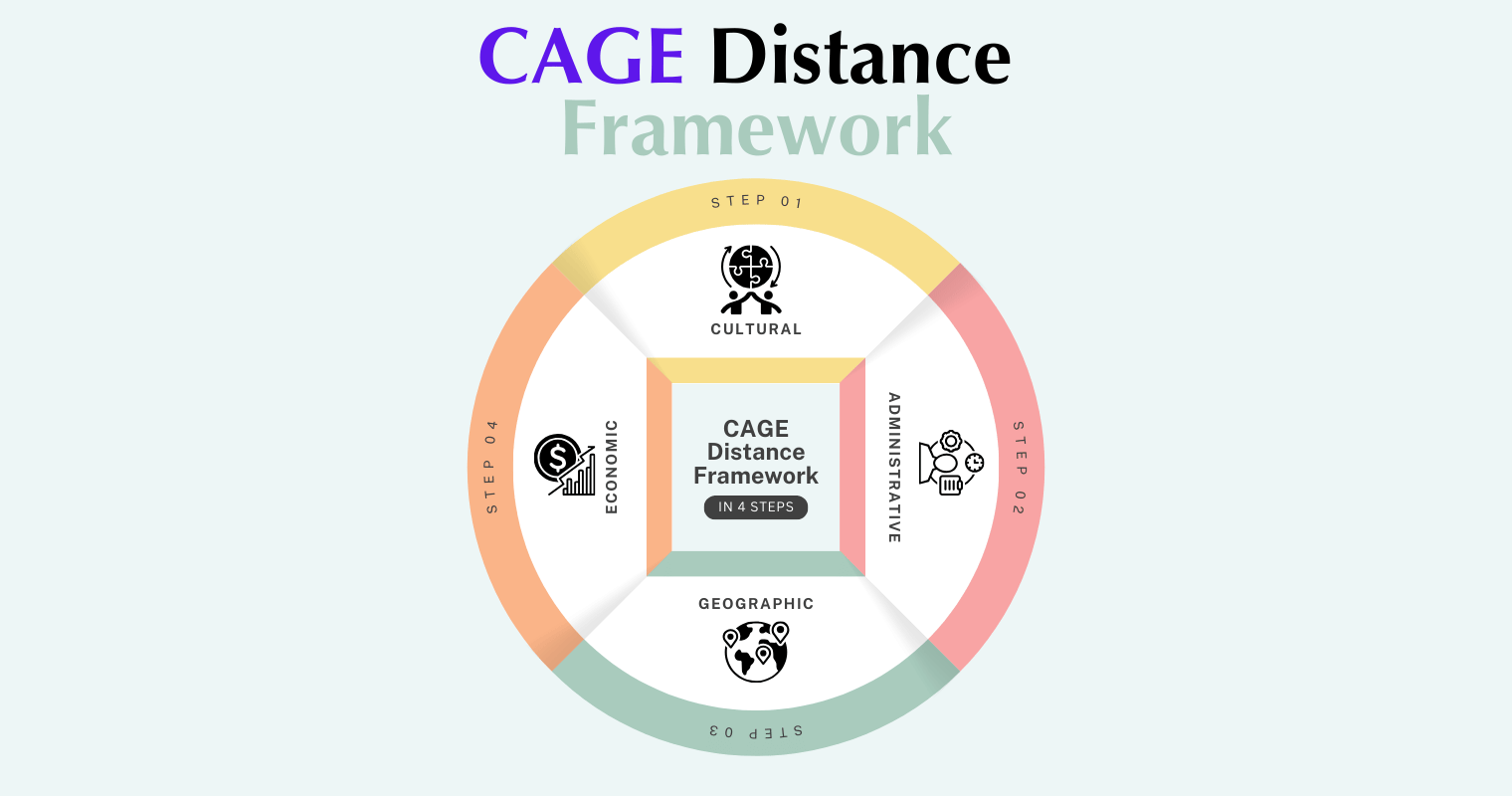
The CAGE Distance Framework was developed by Pankaj Ghemawat in his seminal work “Distance Still Matters.” It is a conceptual tool that provides an assessment of the level of difficulty a company might run into during its entry into a foreign market. The four components comprise:
- Cultural Distance: It refers to the differences in values, beliefs, attitudes, and social norms of the home country in comparison with those of the target market. There is a possibility that such differences may influence everything from marketing strategies to even styles of communication.
- Administrative Distance: It deals with ‘the legal, regulative and bureaucratic differences across nations’. Here, different matters like different tax regimes, labor laws, and intellectual property regimes, and how they affect business operations, figure high in this distance.
- Geographic Distance: This results from the actual distance between the home country and the target market in terms of physical distance. Some problems like transportation costs, differences in time zones, and logistical complexities can present for firms while expanding internationally.
- Economic Distance: This dimension addresses different levels of economic development, infrastructure, and income within countries. Here, these drivers can affect consumer demand, pricing strategies, or even skilled labor availability.
Understanding the Impact of CAGE Distances
According to the CAGE Distance Framework, greater distance on any dimension reflects a more challenging environment for a firm entering a new market. Here, in the below, there is an explanation of how each distance impacts business activities:
- Cultural Distance: Large cultural distances will slightly result in misunderstandings in marketing and communication. Products and services may need to be adapted to local tastes. Likewise, the styles of communication may also need to be modified as per customers or partners to avoid offending.
- Administrative Distance: The extensive quantity of complicated rules and red tape tends to extend business operations and increase costs. This is generally the place where large sums will have to be spent by companies on legal and compliance-related activities.
- Geographic distance: Large physical distances can complicate supply chains and logistics management and make communication with local partners effective. Besides, it imposes a heavy transportation cost.
- Economic Distance: Large economic development differences may influence consumer demand and pricing. So, Firms may adjust their product offerings and pricing models according to the local market.
Applying the CAGE Distance Framework
The following are some possible ways that international business can utilize the CAGE Distance Framework:
- Market selection: Firms can make a better assessment of the potential matches between products and services with target markets by evaluating the CAGE distances between their home country and these other markets.
- Developing Entry Strategies: An understanding of the specific challenges emanating from each distance will aid a company in developing certain strategies that could mitigate those challenges. For example, a firm market entry with a large cultural distance will have to take Cultural Sensitivity training for its employees.
- Building Partnerships: Partnering with a local company would bridge the CAGE gap. So, Local partners can be very instrumental in giving credible insights into the market and help navigate the administrative and cultural terrain.
Limitations of the CAGE Distance Framework
Limitation is borderline for every aspect. Similarly, while most of the framework of CAGE Distance is very useful, however, there are certain limitations to it.
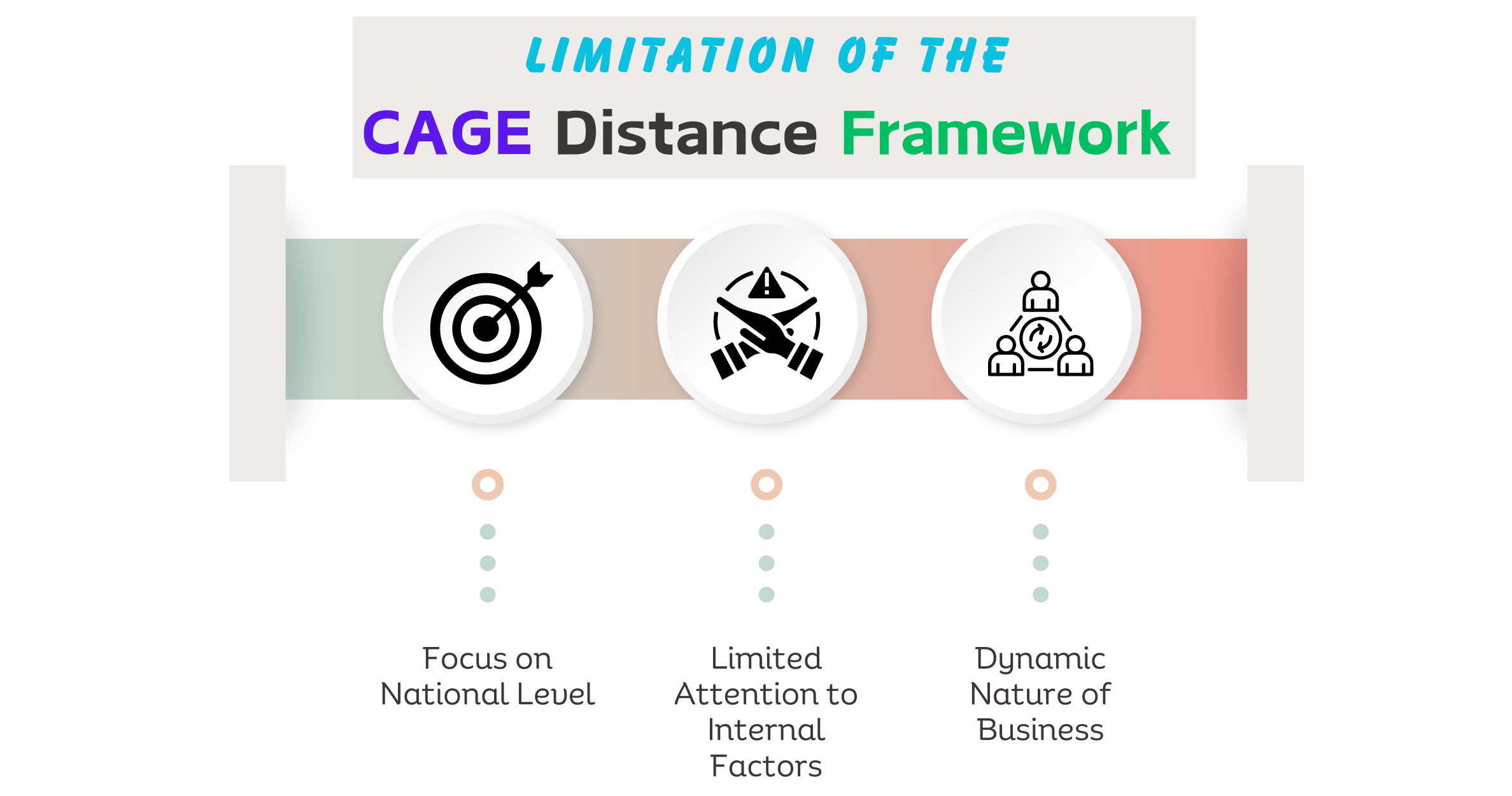
- Focus on National Level: In most cases, it is focused on differences across countries. These differences may not capture the full picture because sub-national variations within countries can be very large.
- Limited attention to internal factors: This framework is oriented toward a consideration of external factors so it has some limitations on specific internal capabilities of the company, like experience in overseas markets or cultural sensitivity.
- Dynamic Nature of Business: Markets are in continuous motion. So, the relative importance of these distances may always vary.
Beyond the CAGE: Additional Considerations for International Business
Though this is built on the CAGE framework, many other drivers and inhibitors can impact the success of business internationally. These include:
- Technological distance: Corporate entry into new markets can be impeded by differences in technology infrastructure and digital adoption across markets.
- Political Distance: The political environment and stability of a country are important components of running a business.
- Legal distance: Legal systemic and intellectual property protection distances create risks across borders for international businesses.
- Competition: The nature and level of competition in a target market may make or break firms.
Conclusion:
The CAGE Distance Framework is a very useful framework that assists international businesses in identifying the challenges of market entry into foreign territories. It helps firms to understand what exactly the challenges are in cultural, administrative, geographic, and economic distances and how to develop relevant strategies to be more effective in foreign markets. Therefore, It would be better applied considering other relevant factors and with a dynamic approach that’s constantly updated about complexities in the global business environment.
Other Related Useful Theories:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
1. Which of the following dimensions are considered in the CAGE Distance Framework?
The CAGE Distance Framework The framework considers four distances that impact entry difficulty either individually or in various combinations in a foreign market. These are:
- Cultural distance: The difference in values, beliefs, attitudes, and social norms prevalent in the home and target countries.
- Administrative Distance: This deals with the distance created concerning existing differences in law, formality, and bureaucracy between two countries.
- Geographic Distance: This implies the physical distance in reality between the home country and the target market.
- Economic distance: This refers to the difference in the degree of development, infrastructure, and per capita income among countries.
2. According to the CAGE Distance Framework, what does cultural distance represent?
Cultural distance is the difference in values, beliefs, attitudes, and social norms between the home country and the target market. A huge cultural distance would manifest setbacks for the trio in communication, marketing strategies, and developing products.
3. CAGE Distance Framework example: Starbucks
Take the case of Starbucks expanding into China. Culturally, there is a strong tradition of tea consumption in China. At an administrative level, food safety and licensing regulations bring in a degree of complexity that Starbucks might have to adhere to. Geographically, the vast size of the Chinese market presents a logistical challenge for supply chains. At an economic level, there could be an income differential in comparison with the US market that would demand price adjustments. Appreciation for those CAGE distances would have helped Starbucks tailor its offerings, get around complex regulations, and chalk out a feasible market entry strategy.
4. How can companies use the CAGE Distance Framework beyond just market selection?
- Entry strategy development: Awareness of exactly which challenges each distance brings helps integrate at each level strategies to reduce them. If, for instance, the administrative distance is large, then partnering with a local company will reduce the problem of dealing with a different regulatory environment.
- Bridge the CAGE gap: Build local partnerships that can bring cultural insight and help guide one through the maze of administrations.
- Resource Allocation: It helps to identify areas where resources can to be pumped in more. Likewise, in terms of resources for culturally diverse employee trainings or more investment in logistics in geographically far-flung markets.