The downstream supply chain is critical in ensuring that finished products are delivered to consumers rapidly and efficiently. These activities range from production to the final delivery of products to customers, including distribution, sales, and customer service. Here, this article will discuss the elements that make up a DSC, how it differs from an upstream supply chain, and why it assumes such a critical role in contemporary business activities.
What is the Downstream Supply Chain?
The downstream supply chain activities and processes denote those that occur after the manufacturing of products; they deal with the final delivery of products to the consumer. It involves the transmission of products through the various channels of purchase, the problems having to do with sales of products and ensuring that consumers are content with the products so that they return to buy. It faces consumers, and it is the one that gives the tools to companies to maintain their stance and goodwill.
Key Components of the Downstream Supply Chain
Distribution
Distribution is the finished goods movement at the selling point or targeted user through either going down to a retailer, wholesaler, or individually in a one-to-one manner. Effective distributing strategies ensure that the merchandise is available where and when it is required.
Sales
The downstream supply chain encompasses sales operations that generate revenues. Here, the downstream supply chain not only means selling. It also has strategies on pricing, promotion, and customer engagement.
Customer Service
Customer support is assistance given to the customer before, during, or after making a sale. Here, Customer Service works as troubleshooting, answering questions, or solving problems to ensure satisfaction.
Logistics
The downstream supply chain deals with logistics that concern the management of the storage, transportation, and delivery of products. This includes warehousing and inventory management with the planning of shipping activities.
Returns Management
Returns management refers to the procedure associated with returned merchandise, whether defective, unsatisfactory, or for other reasons. Here, it is critical in terms of customer trust and the reduction of losses.
Upstream vs. Downstream Supply Chain
Knowing the differences between the upstream and downstream supply chains will help in developing an integrated supply chain management.
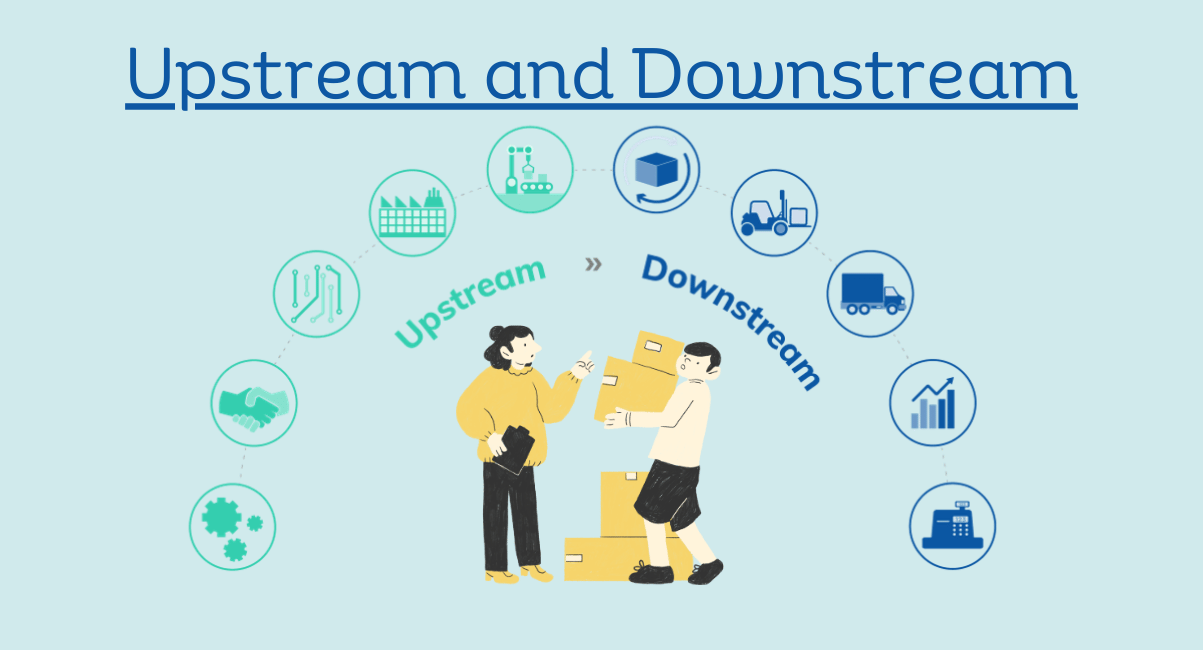
Upstream Supply Chain
- It focuses on the sourcing of raw materials and components needed for production.
- Deals with supplier relationships, purchasing, and inventory.
- This means the primary objective is ensuring a constant supply of inputs to the process of production.
Downstream Supply Chain
- Concerned with the delivery of finished products to consumers.
- It involves distribution, sales, logistics, and customer service.
- The main objectives will be the achievement of product availability and satisfaction of customers.
Upstream supply chain operations deal with the inward flow of raw materials and inputs to the production process, Likewise, DSC activities refer to the outward flow of finished goods into the consumer marketplace. Here, both the Upstream Supply Chain and DSC are interdependent and critical to the overall success of a business.
You Can Also Read: UpStream Supply Chain
The Importance of the Downstream Supply Chain
The downstream supply chain is crucial for several reasons:
Market Penetration
Effective downstream supply chain management ensures wide availability of products and hence helps a business to penetrate different markets and diverse customer bases.
Customer Satisfaction
A well-managed downstream supply chain increases customer satisfaction through on-time delivery, product availability, and quality customer service.
Revenue Generation
Companies are directly influenced in terms of revenue through sales and efficient distribution in the downstream supply chain. In the presence of an efficient downstream process, higher sales and profitability can be achieved.
Brand Loyalty
Companies can establish brand loyalty through great customer service and effective management of returns, which again ensures further purchases and word-of-mouth advertising.
Challenges in the Downstream Supply Chain
Demand Variability
It is tough to predict demand, which puts most businesses in a dilemma of overstocking or stock-outs. Demand forecasting and inventory management are key to balancing supply and demand.
Distribution Complexity
Multiple-channel distribution requires sophisticated logistics and coordination to deliver the products effectively in online and offline markets.
Customer Expectations
With the continuous improvement of e-commerce, buyers have come to expect a short cycle of performance as well as effective return procedures. Managing these expectations while controlling costs is quite a challenge.
Supply Chain Disruptions
This could involve disruptions—natural disasters, transportation strikes, geopolitical events—that hit the downstream supply chain, delaying delivery at higher costs.
Best Practices for Managing the Downstream Supply Chain
To effectively manage the downstream supply chain, companies should consider the following best practices:
Integrated Supply Chain Management
It integrates the upstream and DSC processes in such a way that all of them work harmoniously with one another for better overall efficiency.
Technology Adoption
Technology can aid in optimizing logistics and improving the preciseness of demand forecasting. Better customer service could be achieved through supply chain management software, artificial intelligence, and big data analytics.
Customer-Centric Strategies
It would be possible to achieve better satisfaction and loyalty by focusing on customer needs and preferences; for example, by offering numerous delivery choices and ease of return.
Sustainability Initiatives
Green logistics and distribution reduce carbon emissions and enhance the brand image by minimizing waste produced during packaging.
Continuous Improvement
The downstream processes should be regularly reviewed using techniques such as Lean or Six Sigma, and then optimized for the capture of cost savings and performance improvement.
Conclusion
The downstream portion of the supply chain is, hence, an essential part of the corporate supply chain strategy since it is an area that affects customer satisfaction directly, generates revenues, and builds market presence. It is through distribution, sales, and customer service that companies ensure products efficiently reach consumers to meet market demand.
To effectively drive total supply chain excellence, a fine understanding of the interplay between the upstream and the downstream supply chains is essential. Firms could adopt best practices and use technology in ways that help optimize the DSC from the point of view of remaining competitive in today’s fast-moving marketplace.
FAQ’s
What is the difference between upstream and downstream supply chains?
The upstream supply chain management sources and procures raw materials and components, while the downstream supply chain concerns the process of distributing finished products to consumers and handling customer service. Grasping the difference aids in dealing with both ends effectively.
What are the key activities in the downstream supply chain?
The activities in this element include distribution, sales, logistics, customer service, and returns management. These are the processes by which the products should reach customers efficiently, and customer satisfaction is upheld.
How can companies optimize their downstream supply chain?
Companies have to integrate technology in terms of supply chain management software, logistics, transportation, improvement in customer service, and data analytics for better demand forecasting. This aims at optimizing a downstream supply chain.
Why is the downstream supply chain important for business success?
A downstream supply chain is important in the availability of products to customers, fulfillment of customer demand, and driving revenues. It can also be used in the management of customer satisfaction by improving brand loyalty.
What challenges are commonly faced in the downstream supply chain?
Typical challenges relate to distribution complexity, customer expectations for speed, efficient returns handling, and mitigation of supply chain disruption via strategies like transportation delays or market fluctuation.
References
- Christopher, M. (2016). Logistics & Supply Chain Management (5th ed.). Pearson.
- Hugos, M. (2018). Essentials of Supply Chain Management (4th ed.). Wiley.
- Mentzer, J. T., et al. (2001). Defining Supply Chain Management. Journal of Business Logistics, 22(2), 1-25.




