The upstream supply chain is a very important part of the whole supply chain management process. It enables production to be effective and ensures that the goods are delivered on time. Accordingly, it is important that businesses and any students of supply chain management should understand the dynamics of the upstream supply chain. This article explores the concept of the upstream supply chain, its importance, and the key components that make it function effectively.
What is the Upstream Supply Chain?
Itis the usual procedure for getting raw materials, items, or services essential for the industry’s operations. This term also describes relationships and deals between a business and its vendors along with supply chain management in their delivery to an assembly plant.
It is all about the activities or parties that source raw materials and components necessary for production. It includes the relationships and transactions between a firm and its suppliers, as well as how those materials are moved to the site where they will be used
Key Components of the Upstream Supply Chain
- Supplier Relationships
It management deals with creating strong relationships based on trust. Communication and mutual benefit are the two most essential ingredients of these relationships. Quite often, companies work closely with their suppliers to receive the ‘right material at the right time and the right price’.
- Procurement and Sourcing
This ranges from the selection of suppliers to the actual negotiation of contracts for the actual purchasing of materials needed. On the other hand, some effective sourcing strategies may help bring down the cost, enhance quality, and minimize risk. Many companies, therefore, combine local and global sourcing to attain cost and reliability balances.
- Inventory Management
Proper management of inventory in the upstream supply chain means that there is adequate raw material for production, whereas overstocking ties up capital. An adequate balance between demand and supply is ensured by the company through techniques such as Just-In-Time inventory and safety stock levels.
- Logistics and Transportation
This entails effective logistics and transportation of raw materials from their suppliers to locations of use. It involves the right choice of transportation modes, provision for warehousing, and delivery on time to the production units to forestall delays.
- Quality Control
Quality standards are very high in the upstream supply chain. It will ensure that strict quality criteria are set for suppliers and frequent inspection and audit processes to prove the materials match the specifications.
Upstream vs. Downstream Supply Chain
Knowing the difference between the upstream and downstream supply chains helps manage the supply chain.
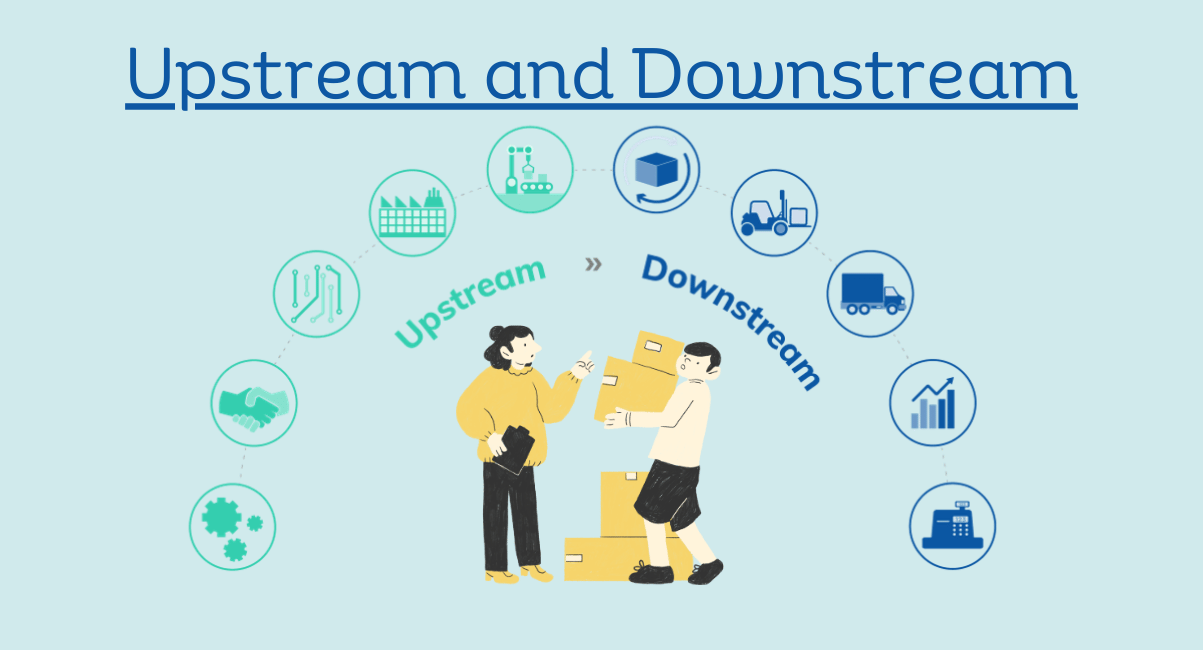
Upstream Supply Chain
- It deals with sourcing raw materials, components, and services from suppliers.
- It involves relationship setting with suppliers, procurement of materials, inventory control, and logistics.
- Key objective: Provide quality raw materials for production.
Downstream Supply Chain
- It involves processes after production: distribution, sales, and customer service.
- It focuses on delivering finished products to consumers.
- Key objective: Satisfaction of customers, products delivered at ease.
Importance of the Upstream Supply Chain
USC is the seed of the entire supply chain process. It obtains the inputs to be used in production, and it therefore has a direct link to impact production efficiency and cost. A well-managed USC may result in:
- Cost Reduction
Through optimized supplier selection, procurement, and logistics, companies can be provided with substantial cost reductions in their productions.
- Improved Quality of Products
Quality consistency in raw materials directly reflects better quality finished goods. So it enhances customer satisfaction and brand reputation for the better..
- Risk Mitigation
Diversification of the supplier base and robust risk management strategies at one’s command may reduce the effect of such supply disruptions, whether due to natural disasters, political instability, or supplier failure.
- Flexibility and Responsiveness
Businesses can react promptly to changes in demand, market conditions, or production schedules by better managing their upstream supply chain and remaining competitive.
Challenges in the Upstream Supply Chain
As the USC comes with importance, management of the upstream supply chain also comes with its own set of challenges.
- Supply Chain Disruptions
Natural disasters, geopolitical events, pandemics, or other disruptions in raw material availability could impact production by delaying it and raising costs.
- Supplier Reliability
Quality materials every time, is an ongoing struggle with suppliers. Companies have to screen their suppliers and make contingency plans just in case things go wrong.
- Cost Fluctuations
Due to changes in market conditions, the prices of the raw materials may fluctuate. This can change the overall cost structure of the company. This can be managed through proper contract management and hedging strategies.
- Sustainability and Compliance
Businesses nowadays are required to source materials in a responsible way, which seeks, in turn, to meet both environmental and social standards. This brings out new complexity into the procurement process yet is quite crucial when it comes to brand reputation and compliance matters.
You can also Real: Economy Shipping
Best Practices for Managing the Upstream Supply Chain
The best practices that companies can use to manage the upstream supply chain are as follows:
- Strategic Supplier Partnerships
Develop long-term collaborative relationships with key suppliers for co-development.
- Technology Integration
Use supply chain management software and technologies like ERP systems and artificial intelligence to manage the inventory transparently.
- Regular Supplier Audits
Regular audits may be carried out to measure compliance with quality and ethics standards.
- Diversification
Do not depend on one supplier or region for critical materials; this reduces risk during disruptions.
- Continuous Improvement
Implementing the processes involved in continuous improvement, like Lean or Six Sigma, can help streamline operations, whereby wastes are minimized or eliminated.
Conclusion
An upstream supply chain is one of the most significant elements in the entire area of supply chain management, as it deals with the sourcing and procurement of raw materials and components necessary for production. Proper comprehension and management of the USC result in cost savings, improved product quality, and decreased risk. For students, educators, and professionals alike, successful command of the UCS will help generally understand the context of supply chain management and the impact of business operations on the same.
References
- Christopher, M. (2016). Logistics & Supply Chain Management (5th ed.). Pearson.
- Handfield, R., & Nichols, E. L. (2002). Supply Chain Redesign: Transforming Supply Chains into Integrated Value Systems. Prentice Hall.
- Mentzer, J. T., DeWitt, W., Keebler, J. S., Min, S., Nix, N. W., Smith, C. D., & Zacharia, Z. G. (2001). Defining Supply Chain Management. Journal of Business Logistics, 22(2), 1-25.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQ’s)
1. What is the upstream supply chain?
It is the usual procedure for getting raw materials, items, or services essential for the industry’s operations.
2. How does the upstream supply chain differ from the downstream supply chain?
It deal with the procurement of raw materials and inputs that will feature in production, while the downstream supply chain involves activities post-production, including distribution, sales, and customer service in getting finished products into the hands of consumers.
3. What are the key components of an effective upstream supply chain?
It comprises relationships with suppliers, procurement and sourcing, inventory management, logistics and transportation, and quality control. All these elements work together to ensure a steady inflow of materials to the manufacturing process.
4. What are the common challenges in managing the upstream supply chain?
Typical challenges include disruptions in the supply chain, the assessment of the reliability of suppliers, cost fluctuation management, and sustainability in the context of maintaining environmental and social standards.
5. How can technology improve the upstream supply chain?
To improve openness, monitor inventory levels, and predict demand, take into account technology like supply chain management, ERP systems, IoT, and artificial intelligence. Upstream supply chains won’t be realized in a more resilient and efficient manner until supplier relationships are strengthened.




